What Was the Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO)?
One of the major features of digital currencies is that they are decentralized. This means they are not controlled by a single institution like a government or central bank, but instead are divided among a variety of computers, networks, and nodes. In many cases, virtual currencies make use of this decentralized status to attain levels of privacy and security that are typically unavailable to standard currencies and their transactions.
Inspired by the decentralization of cryptocurrencies, a group of developers came up with the idea for a decentralized autonomous organization, or DAO, in 2016.1
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The DAO was an organization created by developers to automate decisions and facilitate cryptocurrency transactions.
- In June 2016, due to programming errors and attack vectors, hackers attacked the DAO, accessing 3.6 million ETH.
- Digital exchange currencies de-listed the DAO token in September 2016.
Understanding the Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO)
The DAO was an organization that was designed to be automated and decentralized. It acted as a form of venture capital fund, based on open-source code and without a typical management structure or board of directors. To be fully decentralized, the DAO was unaffiliated with any particular nation-state, though it made use of the ethereum network.
Why make an organization like the DAO? The developers of the DAO believed they could eliminate human error or manipulation of investor funds by placing decision-making power into the hands of an automated system and a crowdsourced process. Fueled by ether, the DAO was designed to allow investors to send money from anywhere in the world anonymously. The DAO would then provide those owners tokens, allowing them voting rights on possible projects.
The DAO launched in late April 2016 thanks to a month-long crowdsale of tokens that raised more than $150 million in funds.2 At the time, the launch was the largest crowdfunding fundraising campaign of all time.
Criticisms of the DAO
By May 2016, the DAO held a massive percentage of all ether tokens that had been issued up to that point (up to 14%, according to reporting by The Economist).3 At roughly the same time, however, a paper was published which addressed several potential security vulnerabilities, cautioning investors from voting on future investment projects until those issues had been resolved.
Later, in June 2016, hackers attacked the DAO based on these vulnerabilities. The hackers gained access to 3.6 million ETH, worth about $50 million at the time.4 This prompted a massive and contentious argument among DAO investors, with some individuals suggesting various ways of addressing the hack and others calling for the DAO to be permanently disbanded. This incident also figured prominently in the hard forking of ethereum that took place shortly thereafter.
According to IEEE Spectrum, the DAO was vulnerable to programming errors and attack vectors.5 The fact that the organization was charting new territory in terms of regulation and corporate law likely did not make the process any easier. The ramifications of the structure of the organization were potentially numerous: investors were concerned that they would be held liable for actions taken by the DAO as a broader organization.
The DAO operated in murky territory about whether or not it was selling securities, as well. Further, there were long-standing issues regarding the way that the DAO would function in the real world. Investors and contractors alike needed to convert ETH into fiat currencies, and this could have impacted the value of ether.
Following the contentious argument over the DAO’s future and the massive hacking incident of earlier in the summer, in September 2016, several prominent digital currency exchanges de-listed the DAO token, marking the effective end for the DAO as it was initially envisioned.67
In July 2017, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued a report, which determined that the DAO sold securities in the form of tokens on the ethereum blockchain, violating portions of US securities law.8
Future of the DAO
What does the future hold for the DAO? The DAO as originally envisioned had not returned as of mid-2020. Nonetheless, interest in decentralized autonomous organizations as a broader group continues to grow. In 2021, The Maker Foundation, an icon in the crypto industry as the original champion of DAO, announced that it was officially turning operations over to MakerDAO (creator of the DAI stablecoin) and would dissolve by the end of the year.9
While there are many lingering concerns and potential issues regarding legality, security, and structure, some analysts and investors believe that this type of organization will eventually come to prominence, perhaps even replacing traditionally structured businesses.
Dash
The popular digital currency Dash is an example of a decentralized autonomous organization because of the way it is governed and the way its budgeting system is structured. It may only be a matter of time before additional DAOs enter the field.
Investing in cryptocurrencies and other Initial Coin Offerings (“ICOs”) is highly risky and speculative, and this article is not a recommendation by Investopedia or the writer to invest in cryptocurrencies or other ICOs. Since each individual’s situation is unique, a qualified professional should always be consulted before making any financial decisions. Investopedia makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or timeliness of the information contained herein. As of the date that this article was written, the author owns cryptocurrencies.
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), sometimes called a decentralized autonomous corporation (DAC),[a] is an organization represented by rules encoded as a computer program that is transparent, controlled by the organization members and not influenced by a central government, in other words they are member-owned communities without centralized leadership.[1][2] A DAO’s financial transaction record and program rules are maintained on a blockchain.[3][4][5] The precise legal status of this type of business organization is unclear.[6]
A well-known example, intended for venture capital funding, was The DAO, which amassed $150 million in crowdfunding in May 2016, and was hacked and drained of US$50 million in cryptocurrency weeks later.[7] The hack was reversed in the following weeks, and the money restored, via a hard fork of the Ethereum blockchain. Most Ethereum miners and clients switched to the new fork while the original chain became Ethereum Classic.
Background
Decentralized autonomous organizations are typified by the use of blockchain technology to provide a secure digital ledger to track digital interactions across the internet, hardened against forgery by trusted timestamping and dissemination of a distributed database.[3][4][8] This approach eliminates the need to involve a mutually acceptable trusted third party in any decentralized digital interaction or cryptocurrency transaction.[4] The costs of a blockchain-enabled transaction and of the associated data reporting may be substantially offset by the elimination of both the trusted third party and of the need for repetitive recording of contract exchanges in different records. For example, the blockchain data could, in principle and if regulatory structures permit it, replace public documents such as deeds and titles.[3]: 42 [4] In theory, a blockchain approach allows multiple cloud computing users to enter a loosely coupled peer-to-peer smart contract collaboration.[3]: 42 [9]
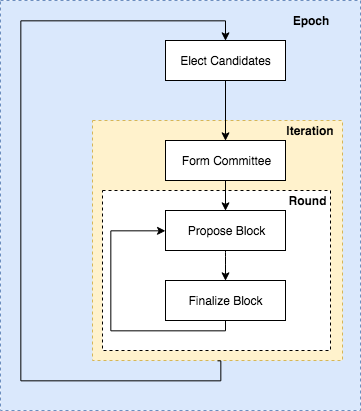
Vitalik Buterin proposed that after a DAO is launched, it might be organized to run without human managerial interactivity, provided the smart contracts are supported by a Turing-complete platform. Ethereum, built on a blockchain and launched in 2015, has been described as meeting that Turing threshold, thus enabling such DAOs.[3][10][11] Decentralized autonomous organizations aim to be open platforms through which individuals control their identities and their personal data.[12]
Governance
DAO governance is coordinated using tokens or NFTs that grant voting powers. Admission to a DAO is limited to people who have a confirmed ownership of these governance tokens in a cryptocurrency wallet, and membership may be exchanged. Governance is conducted through a series of proposals that members vote on through the blockchain, and the possession of more governance tokens often translates to greater voting power. Contributions from members towards the organizational goals of a DAO can sometimes be tracked and internally compensated. Inactive holders of governance tokens can be a major obstacle for DAO governance,[5] which has led to implementations of allowing voting power to be delegated to other parties.
Issues
Social
Inactive or non-voting shareholders in DAOs often disrupt the organization’s possible functionality.[5]
Legal status, liability, and regulation
The precise legal status of this type of business organization is generally unclear,[8] and may vary by jurisdiction. On July 1, 2021, Wyoming became the first US state to recognize DAOs as a legal entity.[13] American CryptoFed DAO became the first business entity so recognized.[14] Some previous approaches to blockchain based companies have been regarded by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission as illegal offers of unregistered securities.[6][15] Although often of uncertain legal standing, a DAO may functionally be a corporation without legal status as a corporation: a general partnership.[16] Known participants, or those at the interface between a DAO and regulated financial systems, may be targets of regulatory enforcement or civil actions only if they are out of compliance with the law.[16]
Security
A DAO’s code is difficult to alter once the system is up and running, including bug fixes that would be otherwise trivial in centralized code. Corrections to a DAO require writing new code and agreement to migrate all the funds. Although the code is visible to all, it is hard to repair, thus leaving known security holes open to exploitation unless a moratorium is called to enable bug fixing.[17]
In 2016, a specific DAO, “The DAO“, set a record for the largest crowdfunding campaign to date.[18][19] Researchers pointed out multiple problems with The DAO’s code. The DAO’s operational procedure allowed investors to withdraw at will any money that had not yet been committed to a project; the funds could thus deplete quickly.[5] Although safeguards aimed to prevent gaming shareholders’ votes to win investments,[6] there were a “number of security vulnerabilities”.[20] These enabled an attempted large withdrawal of funds from The DAO to be initiated in mid-June 2016.[21][22] On July 20, 2016, the Ethereum blockchain was forked to bail out the original contract.
DAOs can be subject to coups or hostile takeovers that upend its voting structures especially if the voting power is based upon the number of tokens one owns. An example of this occurred in 2022, when Build Finance DAO suffered a coup in which one person amassed enough tokens to get a vote passed, then voted to give themselves full control of the DAO, then, using this power, they drained all of the money from the DAO.[23]
List of notable DAOs
| Name | Token | Use cases | Network | Launch | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dash | DASH | Governance, fund allocation [24] | Dash (cryptocurrency) | May 2015[25] | Operational since 2015[26][27][28] |
| Steem | STEEM | Data distribution, Social media, Name services, Industrial | Steem | March 2016 | Operational |
| The DAO | DAO | Venture capital | Ethereum | April 2016 | Defunct late 2016 due to hack[29] |
| Augur | REP | Prediction market, Sports betting, Option (finance), Insurance | Ethereum | July 2018 | Operational |
| Uniswap | UNI | Exchange, Automated Market Making | Ethereum | November 2018 | Operational[30] |
| BitDAO | BitDAO | Build the future of finance in a decentralized way. | Ethereum | August 2021 | Operational[31] |
| ConstitutionDAO | PEOPLE | Purchasing an original copy of the Constitution of the United States | Ethereum | November 2021[32] | Defunct[33] |
| AssangeDAO | $JUSTICE[34] | Purchased Clock, an NFT artwork by Pak, to fund legal defense of WikiLeaks‘ founder Julian Assange | Ethereum | February 2022[35] | Operational |
See also
- Decentralized application
- Decentralized computing
- Distributed computing
- Incentive-centered design
- List of highest funded crowdfunding projects
- Smart contract
- The Social Contract
- Open value network
Notes
- ^ Depending on English dialect, it may also be spelled decentralised autonomous organisation. The terms decentralized autonomous company, distributed autonomous organization, etc., have also been used.
References
- ^ Prusty, Narayan (27 April 2017). Building Blockchain Projects. Birmingham, UK: Packt. p. 9. ISBN 9781787125339.
- ^ The Decentralized Autonomous Organization and Governance Issues Regulation of Financial Institutions Journal: Social Science Research Network (SSRN). 5 December 2017.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e Vigna, P.; Casey, M. J. (27 January 2015). The Age of Cryptocurrency: How Bitcoin and the Blockchain Are Challenging the Global Economic Order. St. Martin’s Press. ISBN 9781250065636.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d Hodson, H. (20 November 2013). “Bitcoin moves beyond mere money”. New Scientist.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d “The DAO of accrue: A new, automated investment fund has attracted stacks of digital money”. The Economist. 21 May 2016.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c Popper, N. (21 May 2016). “A Venture Fund with Plenty of Virtual Capital, but No Capitalist”. New York Times.
- ^ Price, Rob (17 June 2016). “Digital currency Ethereum is cratering amid claims of a $50 million hack”. Business Insider. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Wright, A; De Filippi, P. (10 March 2015). “Decentralized Blockchain Technology and the Rise of Lex Cryptographia”. SSRN 2580664.
- ^ Norta, A. (18 August 2015). “Creation of Smart-Contracting Collaborations for Decentralized Autonomous Organizations”. Perspectives in Business Informatics Research. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing. Vol. 229. pp. 3–17.
- ^ Pangburn, D. J. (19 June 2015). “The Humans Who Dream of Companies That Won’t Need Us”. FastCompany.
- ^ Evans, J. (1 August 2015). “Vapor No More: Ethereum Has Launched”. TechCrunch.
- ^ Deegan, P. (2014). “Chapter 14—The Relational Matrix: The Free and Emergent Organizations of Digital Groups and Identities”. In Clippinger, J. H.; Bollier, D. (eds.). From Bitcoin to Burning Man and Beyond: The Quest for Identity and Autonomy in a Digital Society. Amherst, Massachusetts: Institute for Institutional Innovation. pp. 160–176. ISBN 978-1-937146-58-0.
creating an operational and autonomous Trust Framework [that can i]ntegrate with a secure discovery service in the form of a Decentralized Autonomous Organization …
- ^ “Decentralized Autonomous Organizations Find a Home in Wyoming”. JD Supra. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ^ “Wyoming becomes first US state to legally recognise DAO”. finance.yahoo.com. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ^ “SEC Charges Bitcoin Entrepreneur With Offering Unregistered Securities”. US Securities and Exchange Commission. 3 June 2014.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Levine, M. (17 May 2016). “Blockchain Company Wants to Reinvent Companies”. Bloomberg View: Wall Street. Bloomberg News.
- ^ Peck, M. (28 May 2016). “Ethereum’s $150-million Blockchain-powered Fund Opens Just as Researchers Call For a Halt”. IEEE Spectrum. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
- ^ Vigna, P. (16 May 2016). “Chiefless Company Rakes in More Than $100 Million”. Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Waters, R. (17 May 2016). “Automated company raises equivalent of $120M in digital currency”. Financial Times.
- ^ Popper, N. (27 May 2016). “Paper Points Up Flaws in Venture Fund Based on Virtual Money”. The New York Times.
- ^ Popper, N. (17 June 2016). “Hacker May Have Taken $50 Million From Cybercurrency Project”. New York Times.
- ^ Price, R. (17 June 2016). “Digital currency Ethereum is cratering amid claims of a $50 million hack”. Business Insider. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ “Democratic DAO Suffers Coup, New Leader Steals Everything – VICE”. www.vice.com. Retrieved 16 February 2022.
- ^ Duffield, Evan (22 April 2015). “Self-sustainable Decentralized Governance by Blockchain”. dash.org/forum.
- ^ Duffield, Evan (14 May 2015). “GitHub commit adding Dash DAO feature”. github.com/dashpay. Retrieved 7 April 2021.
- ^ Duffield, Evan (28 August 2015). “Budgets Are Live”. dash.org/forum.
- ^ Engelhorn, Philipp (7 September 2015). “First 3 Superblocks!”. dash.org/forum. Retrieved 7 April 2021.
- ^ “First Blockchain DAO payout”. blockchair.com/dash. 7 September 2015. Retrieved 7 April 2021.
- ^ Finley, Klint (18 June 2016). “Someone Just Stole $50 Million from the Biggest Crowdfunded Project Ever (Humans Can’t Be Trusted)”. Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
- ^ “OpenOrgs.info”. openorgs.info. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ “BitDAO price today, BIT to USD live, marketcap and chart”. CoinMarketCap. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ^ Roose, Kevin (17 November 2021). “They Love Crypto. They’re Trying to Buy the Constitution”. The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- ^ Fox, Matthew (19 January 2022). “Tokens of the defunct DAO that failed to buy a copy of the constitution are worth $300 million even after disbanding”. news.yahoo.com. Retrieved 28 January 2022.
- ^ “Justice Token”. AssangeDAO. Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- ^ Reuters (9 February 2022). “‘Cypherpunks have rallied to Assange’: NFT auction raises $52m for WikiLeaks founder”. The Guardian.